Disclaimer: This website provides health information for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a psychological condition resulting from a traumatic event.
- Common symptoms of PTSD include re-experiencing the trauma, avoidance, hyperarousal, negative moods, and physical symptoms.
- Risk factors for PTSD include low social support, a history of traumatic events, and previous mental health issues.
- Treatment options for PTSD include rehabilitation programs, outpatient treatment, medications, and self-help strategies.
- It is important to seek help if you or someone you know is struggling with PTSD. With the right support, those with PTSD can find healing and lead a healthy life.
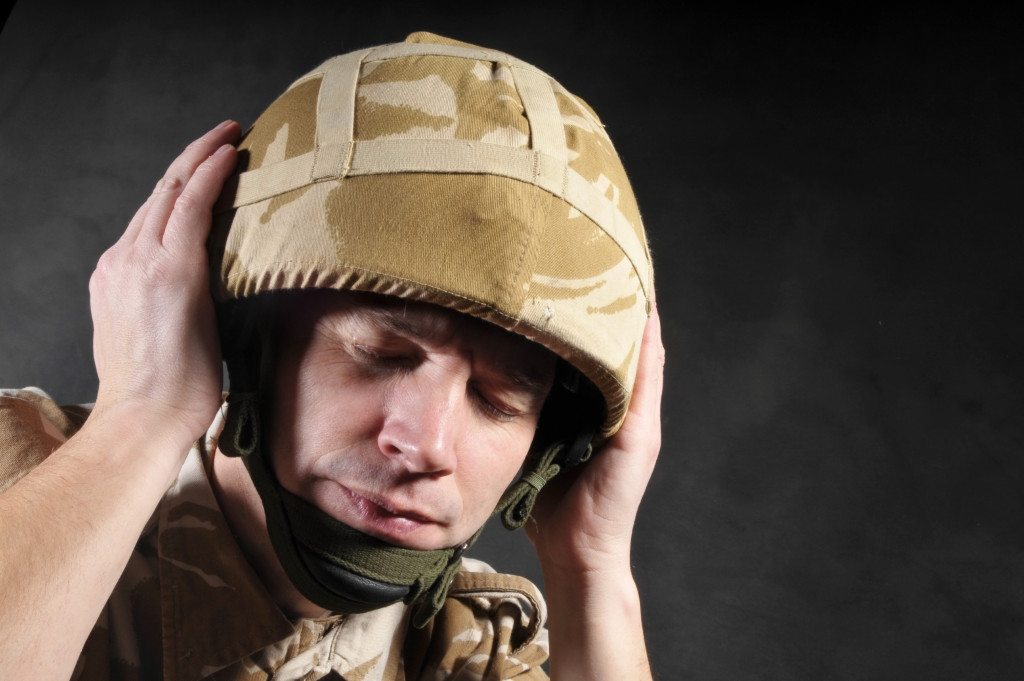
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a severe psychological condition resulting from exposure to a traumatic event. It can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, social status, or background. People with PTSD experience many symptoms, some of which can be alarming and overwhelming. Here are the most common symptoms of PTSD and how to recognize and manage them.
What is PTSD?
PTSD is a psychiatric disorder that can occur after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event such as war, natural disasters, serious accidents, physical/sexual violence, etc. People exposed to these events may experience fear, helplessness, and horror. It’s estimated that 5% of the overall adult population in the U.S. have this disorder. Here are its symptoms:
Re-experiencing Symptoms
One of the most common symptoms of PTSD is re-experiencing the traumatic event. This can take many forms, from flashbacks to nightmares, intrusive thoughts, or overwhelming feelings of distress when reminded of the trauma. It can happen anytime, often triggering intense reactions such as sweating, shaking, or hyperventilating.
Avoidance Symptoms
Avoidance is another significant PTSD symptom. People with PTSD often avoid anything that reminds them of the trauma, such as places, people, or situations. They may also try to numb their emotions by using drugs or alcohol or withdraw from social interactions altogether. This can lead to isolation, depression, and feelings of hopelessness.
Hyperarousal Symptoms
Hyperarousal is a state of constant alertness, which many people with PTSD experience. They may feel irritable, angry, or easily startled and have trouble concentrating or sleeping. Hyperarousal symptoms can be very distressing and interfere with daily functioning.
Negative Mood Symptoms
People with PTSD may also experience negative mood symptoms like depression, guilt, or shame. These feelings can be persistent and overwhelming, often leading to a loss of interest in once-used activities. Negative mood symptoms can make it challenging to seek help, but it’s important to remember that effective treatment is available.

Physical Symptoms
PTSD can also affect the body, and people with this condition may experience physical symptoms such as headaches, stomach aches, or chest pain. These symptoms can be caused by stress, anxiety, or tension and are often debilitating. Seeking treatment for PTSD can help alleviate these symptoms and restore physical well-being.
Risk Factors
PTSD has various risk factors. Here are some of them:
Low Social Support
Those who don’t have a strong social support system or close relationships may be more likely to develop PTSD. Lack of support can also make seeking help and getting the necessary treatment harder.

History of Traumatic Events
Research has shown that those with a history of traumatic events are more likely to experience PTSD after another event. This is because they may be more vulnerable and have difficulty recovering.
Previous Mental Health Issues
An existing mental health issue can increase the risk of developing PTSD after a traumatic event. It’s important to seek help if you struggle with your mental health before, during, or after a traumatic event.
Treatment
There are various treatments you can take for PTSD. Here are some of them:
Rehab
Soldiers and victims of sexual assault may be eligible for specialized treatment programs that provide psychological and medical support. Rehab is one of the best ways to get the help you need and start recovering.
Outpatient Treatment Options
You have other options if you don’t want to go to rehab. An experienced intensive outpatient therapist can help you with your therapy. They can use techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, or mindfulness-based therapies to help you work through your trauma.
Medication
A few medications can be used to treat PTSD symptoms, including antidepressants and anti-anxiety medication. It’s important to talk with your doctor about the pros and cons of taking medication for your PTSD.
Self-Help Strategies
There are also self-help strategies you can use to help manage the symptoms of PTSD. These include relaxation techniques, physical activities, and support groups. You can also practice mindfulness exercises or try writing in a journal to deal with emotions and thoughts related to the trauma.
If you or someone you know is struggling with PTSD, it’s important to seek help. Many resources are available to get the necessary treatment and take the steps needed to move forward. With the right support, those with PTSD can find healing and lead a healthy life.