Disclaimer: This website provides health information for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have.
- Regular exercise and stretching can help to reduce back pain.
- Maintaining proper posture is important for reducing strain on the back muscles and joints.
- Heat and cold therapy can be effective in reducing back pain.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage chronic back pain but should not be overused.
- Regular screenings and tests can help identify any underlying medical conditions causing the pain.
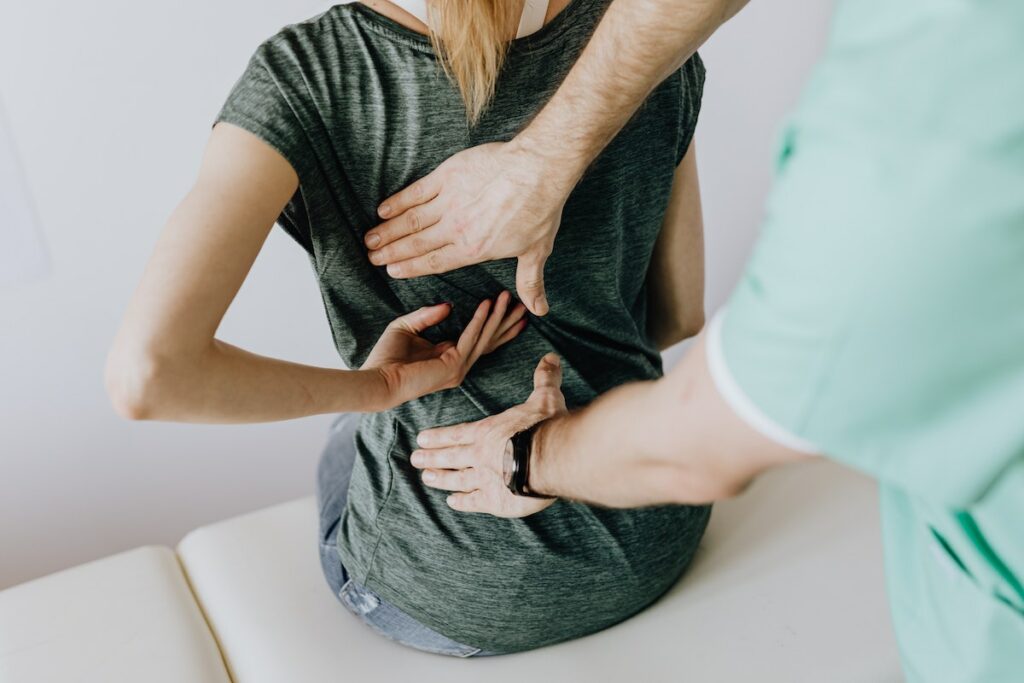
Chronic back pain is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can significantly impact your quality of life, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks or even participate in activities you enjoy. However, there are steps you can take to manage and alleviate the pain, allowing you to lead a more comfortable life. This guide will provide you with five tips on managing chronic back pain.
1. Engaging in Regular Exercise and Stretching
Regular exercise and stretching can help to improve back pain by increasing strength, flexibility, and mobility. Low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, and yoga can effectively manage chronic back pain. However, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting a new exercise regimen to avoid any further injury.
2. Maintaining Proper Posture

Poor posture can contribute to back pain, especially if you sit or stand for extended periods. Maintaining proper posture can help reduce stress on your back muscles and joints. When sitting, ensure your feet are flat on the ground and your back is straight. Keep your shoulders back and your weight evenly distributed between your feet when standing.
If you must stand for prolonged periods, try to keep one foot slightly in front of the other and alternate feet every few minutes. Use a chair with armrests to reduce strain on your shoulders and arms. When lifting objects, bend at the knees and use your leg muscles, not your back. By adhering to proper posture habits, you can help support your spine and reduce the risk of back pain.
3. Utilizing Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapy can be effective in reducing back pain. Heat therapy, such as a warm bath or heating pad, can help increase blood flow and relax muscles. Cold therapy, such as an ice pack, can help reduce inflammation and swelling.
When using heat, be sure to set the temperature at a comfortable and not too hot level. Wrap the ice pack in a thin cloth or towel before placing it on the skin for cold therapy. Both forms of therapy should only be used for 15-20 minutes at a time to avoid skin irritations or burning. Additionally, consult with a doctor before beginning any form of heat or cold therapy as it may not be suitable for certain medical conditions.
4. Taking Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can effectively manage chronic back pain. However, following the recommended dosage and not relying on medication as the sole solution for pain relief is essential.
5. Getting Screenings and Tests
Chronic back pain can sometimes indicate a more severe underlying condition. Regular screenings and tests can help identify any issues before they become more severe.
Here are some screening and tests you can utilize:
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests can help determine the cause of your back pain. An open upright MRI test is an advanced imaging technique that allows you to sit comfortably while providing detailed spine images. This test can provide valuable information about any potential structural issues that may be causing your chronic back pain and allow for more accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Physical Exam
A physical exam with your healthcare provider is important for determining what type of back pain you have and what treatment plan best suits your pain. During the physical exam, they will observe your posture and range of motion to diagnose what’s happening inside your body.
Blood Tests

Blood tests can screen for conditions that might cause chronic back pain or other health concerns such as arthritis or anemia. Sometimes, your doctor may order additional tests to confirm their diagnosis.
Bone Density Test
Osteoporosis is a common cause of chronic back pain in older adults and can be detected with a bone density test. This test measures the amount of calcium and other minerals in your bones to determine if you are at risk for developing osteoporosis or already have it.
Muscle and Nerve Tests
If there appears to be nerve damage causing your back pain, your doctor might order an electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction study (NCS) to help diagnose the problem. An EMG measures electrical activity in your muscles, while an NCS measures electrical impulses traveling along nerves. These tests can detect any nerve damage or other medical conditions causing the pain.
In Summary
Chronic back pain can be a challenging condition to manage, but there are steps you can take to reduce pain and improve your quality of life. Incorporating exercise, maintaining proper posture, using heat and cold therapy, and taking medication can effectively manage pain. Additionally, it is crucial to get regular screenings and tests to identify any underlying conditions that may be contributing to your pain. By following these tips and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can manage your chronic back pain and enjoy a more comfortable life.