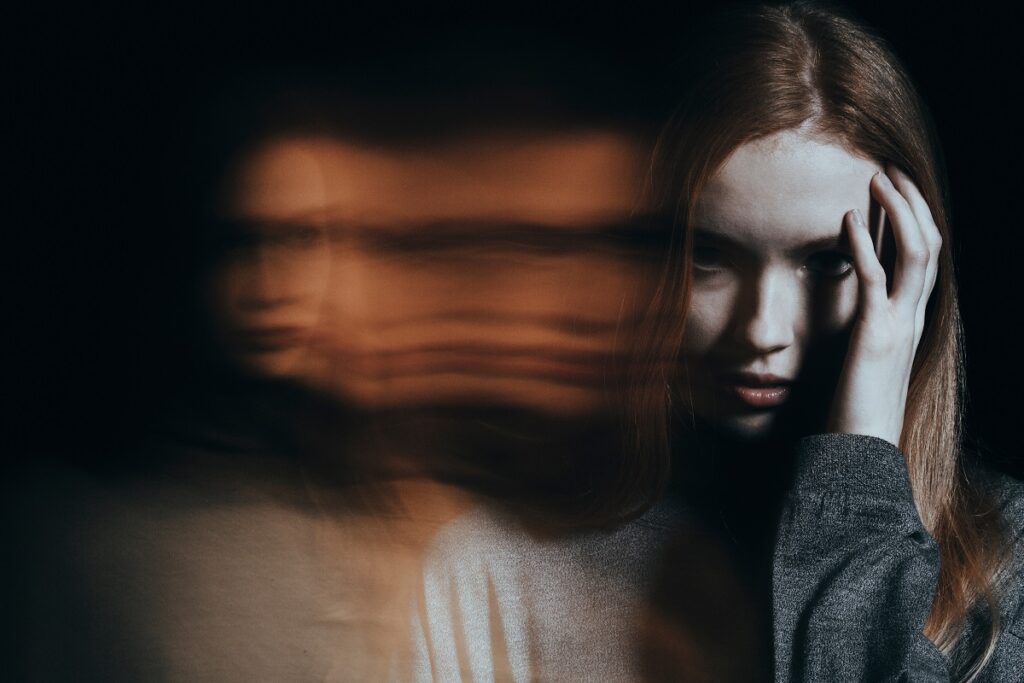
- Schizophrenia is a mental disorder that affects elderly individuals.
- Genetics, brain abnormalities, substance abuse, and chronic medical conditions may increase the risk of schizophrenia in later life.
- Preventative measures include regular scans, exercise, healthy eating habits, social connectedness, and coping strategies.
- Early diagnosis is essential for successful treatment outcomes.
- Seek professional help if signs of schizophrenia are present.
As people age, they become more vulnerable to physical and mental health problems. One of the most challenging issues that elderly individuals face is schizophrenia. Schizophrenia can affect how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. Although this condition is commonly associated with young adults, it can also manifest in seniors.
As a caregiver, family member, or healthcare professional, it’s essential to understand the underlying causes of schizophrenia in older individuals.
What is Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a chronic mental disorder that affects a person’s cognition. It is characterized by symptoms that can include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking and speech, social withdrawal, and impaired cognitive functioning. It’s estimated that there are 685,000 people with schizophrenia in the U.K. alone.
Genetics

Studies reveal that genetics plays a crucial role in developing schizophrenia in people of all ages. Individuals with a family history of the disease are more likely to have it than those without. If an older individual has a sibling, parent, or child with schizophrenia, they are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Additionally, a DNA strand known as the COMT gene is associated with an increased risk of schizophrenia.
Brain Abnormalities
Experts suggest that brain structure and function changes could lead to schizophrenia in old age. As people age, certain parts of the brain atrophy, which could affect the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Abnormalities in the brain’s dopamine and glutamate systems may also contribute to the development of this disorder.
Substance Abuse
Older adults may abuse drugs or alcohol to cope with stress, loneliness, or depression. Substance abuse can damage the brain, increase the risk of dementia, and trigger mental health disorders such as schizophrenia. Moreover, drug-induced psychosis is a common phenomenon that mimics schizophrenia symptoms like delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized thinking.
Chronic Medical Conditions
Older adults may suffer from chronic health conditions such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes, or Parkinson’s disease. Some of these conditions may require medication, which may have side effects that affect mental health. For example, some Parkinson’s disease drugs can cause psychosis, while steroids used to treat autoimmune disorders can trigger manic episodes.
Social Isolation
Due to retirement, the loss of loved ones, and reduced mobility, older adults are at risk of social isolation and loneliness. Social isolation can significantly impact mental health, leading to anxiety, depression, and psychosis. Moreover, social withdrawal can exacerbate cognitive and sensory impairments, leading to a misdiagnosis of schizophrenia.
How to Prevent Schizophrenia Among Seniors
Thankfully, there are various ways you can prevent schizophrenia. Here are five ways to do that:
Get Scanned Every Two Years

Certain medical scans can now identify the onset of neurological and psychological disorders such as schizophrenia. One of the most effective medical scans is a private CT scan. This scan looks into the brain tissue and can identify any changes that might be linked to mental disorders.
Encourage Regular Exercise
Physical activity is vital in preventing schizophrenia by improving blood flow to the brain and boosting serotonin levels. Encouraging seniors to stay active by going on daily walks or participating in a sport benefits their overall health and well-being.
Encourage Healthy Eating Habits
Following a healthy diet can help reduce the risk of schizophrenia. Incorporate fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains into your elderly loved one’s diet. Avoid processed foods, excessive sugar intake, trans fats, and caffeine, as these have been linked to mood swings and disturbed sleep patterns.
Promote Social Connectedness
Seniors should be encouraged to stay socially connected and engage in meaningful activities. Participate in group activities such as attending classes, joining a book club, or playing a team sport. These can help reduce social isolation and loneliness, which can trigger mental health issues.
Encourage Healthy Coping Strategies
It is essential to teach your elderly loved ones healthy coping strategies to help them manage stress and anxiety. Encourage them to seek professional help and practice relaxation techniques like breathing exercises or mindfulness meditation.
By following these five steps, you can prevent schizophrenia among seniors and ensure they live happy and healthy lives. Moreover, early diagnosis of the disorder is critical for successful treatment outcomes. If you are concerned that your elderly loved one may show signs of schizophrenia, seek professional help immediately.